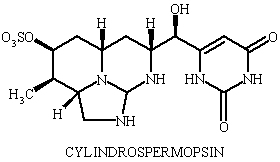
Although originally described from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, cylindrospermopsin can be found also in Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Umezakia natans. The toxin is a cyclic alkaloid and, like microcystins, primarily affects the liver, although causes considerable damage to other major organs. Its LD50 (i.p., mice) of 200 µg kg-1ranks it as a relatively potent cyanobacterial toxin.